ELECTRICITY
CBSE CLASS 10TH
SCIENCE
CHAPTER 12
ELECTRICITY
To study concept of electricity we require the knowledge of behavior of materials and charges etc which we have studied in the lower classes.
To make a true concept of chapter electricity in our mind.We will start with behavior of materials.
Materials are classified for study of electricity into two categories:
- Conductor
- Insulators.
S N
|
Property
|
Conductor
|
Insulator
|
1
|
Flow of charge
|
can flow
|
can not flow
|
2
|
Free electrons
|
Present in huge amount
|
Present in less amount (negligible)
|
3
|
Charging
|
can not be charged
|
can be charged
|
4
|
Example
|
copper, aluminium etc.
|
plastic , wood, rubber etc.
|
Electric Charge (Q or q):
Electric Charge is the physical property of a substance which cause it to exert as well as to experience a electric force when placed near some other substance.S I unit of electric charge is Coulomb (C).
It is a scalar quantity.
Mathematically, Q=ne, e= -1.6 x 10-19 C and n can be any integer.
Types of Charges: a) positive charge b) negative charge.
Cause of Electrification: Due to transfer of electrons.
Total charge in universe always remains constant. Electric charge always remains conserved, obeys law of conservation.
Electric Current = Charge/Time
One Ampere is defined as flow of one coulomb of charge in one second through a conductor.
1 A= 1 C/1s
Other Small units: 1 milli Ampere = 10-3 A, 1 micro Ampere = 10-6 A, 1 nano Ampere = 10-9 A.
Electric current is a scalar quantity.
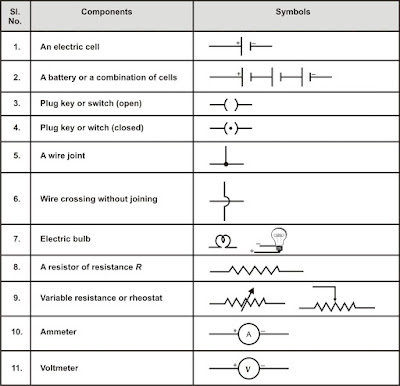
Electric Current is measured by a device called Ammeter. Ammeter is always joined in series in a circuit. It has low resistance. And ideal ammeter has zero resistance.
Electric Current(I):
Electric Current is the average charge passing through an area of cross-section in a given time.
OR
It is rate of flow of charge per unit time in a conductor.
Electric current is denoted by 'I'.OR
It is rate of flow of charge per unit time in a conductor.
Electric Current = Charge/Time
I=Q/t.
I= ne/t.
S I unit of electric current is Ampere (A).One Ampere is defined as flow of one coulomb of charge in one second through a conductor.
1 A= 1 C/1s
Other Small units: 1 milli Ampere = 10-3 A, 1 micro Ampere = 10-6 A, 1 nano Ampere = 10-9 A.
Electric current is a scalar quantity.
Electric Current is measured by a device called Ammeter. Ammeter is always joined in series in a circuit. It has low resistance. And ideal ammeter has zero resistance.
CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE CHAPTER 12 ELECTRICITY NOTES
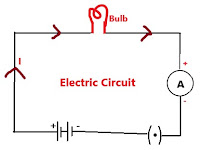
Electric Circuit :
A closed and continuous path of electric current is known as electric circuit.
Component of circuit:
 |
| Electric Circuit |
 | |
|
Direction of flow of current:
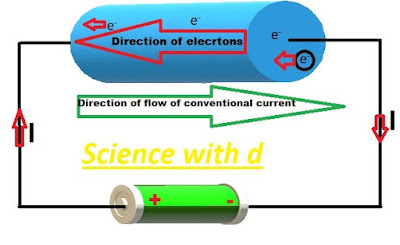
At the time when phenomenon of electricity was observed, electron's were not yet discovered so at that time it was considered as flow of positive charge from positive to negative terminal of battery known as conventional current.
 |
| Direction of flow of current |
Direction of conventional current is from higher to lower potential .
From positive to negative terminal of battery.
Opposite to the flow of electrons.
CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE CHAPTER 12 ELECTRICITY NOTES
CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE CHAPTER 12 ELECTRICITY NOTES
NEXT TOPIC: ELECTRICITY PART 2 OHM'S LAW
Question/Numerical based on topics:
Q Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
Ans Given Q = 1 C
Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19C
Q= ne
n=Q/e
n=1/1.6 x 10-19 = 1 x 1019/1.6=10 x 1019/16=100 x 1018/16 =6.25 x 1018electrons
Q If two micro coulomb of charge is following in a circuit for 5 minute. What is the amount of current in the circuit.
Ans Given Charge = two micro coulomb = 2 x 10-6C
Time = 5 minute = 5 x 60 = 300 s
Current I = Q/t= 2 x 10-6C /300 s = 0.667 x 10-8 A = 6.67 x 10-9A



Comments
Post a Comment