CBSE Physics paper class 12th
CBSE PHYSICS PAPER CLASS 12th JULY 2019
 |
| CBSE PHYSICS QUESTION PAPER JULY 2019 |
MM: 70 Time: 3 Hr
SECTION A (1 Marks Questions)
Q 1. Define the angle of inclination at a given place due to earth’s magnetic field.
Q 2. Name the most energetic electromagnetic radiation and write its frequency range.
Name the electromagnetic radiation used in eye surgery or to kill germs in water purifiers. Write its frequency range.
Q 3. Estimate the frequency associated with a photon of energy 2 eV.
OR
Q 3. Estimate the frequency associated with a photon of energy 2 eV.
OR
In photoelectric effect, does the photoelectric current depend on the intensity of incident radiation ? Give reasons.
Q 4. Which property of nuclear force explains the approximate constancy of binding energy per nucleon with mass number A for nuclei in the range 30 < A < 170 ?
Q 5. Define the term ‘band width’ of message signals in communication system.
Q 4. Which property of nuclear force explains the approximate constancy of binding energy per nucleon with mass number A for nuclei in the range 30 < A < 170 ?
Q 5. Define the term ‘band width’ of message signals in communication system.
SECTION B (2 Marks Questions)
Q 6. An electric field along the x-axis is given by  N/C for x > 0 and
N/C for x > 0 and  N/C for x < 0. A right circular cylinder of length 20 cm and radius 5 cm lies parallel to the x-axis, with its center at the origin and one face at x = + 10 cm, the other face at x = – 10 cm. Calculate the net outward flux through the cylinder.
N/C for x < 0. A right circular cylinder of length 20 cm and radius 5 cm lies parallel to the x-axis, with its center at the origin and one face at x = + 10 cm, the other face at x = – 10 cm. Calculate the net outward flux through the cylinder.
Q 7. In a ceiling fan, each blade rotates in a circle of radius 0·5 m. If the fan makes 2 rotations per second and the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field is 8 x 10-5 T, calculate the emf induced between the inner and outer ends of each blade.
OR
A square loop of side 10 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is moved with a velocity of 8 cm s-1 in the positive X-direction containing a magnetic field in the positive Z-direction. The field is non-uniform and has a gradient of 10-3 T cm-1 along the negative X-direction (i.e. it increases by 1 T cm-1 as one moves in the negative X- direction). Calculate the emf induced.Q 8. a) Draw a graph of a linearly polarized em wave propagating in the z-direction showing the directions of the oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
b) Write the relations (i) between the speed of light and the amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields, (ii) for the speed of em wave in terms of a permittivity εo, and magnetic permeability μo, of the medium.
Q 9. Estimate the ratio of the wavelengths associated with the electron orbiting around the nucleus in the ground and first excited states of hydrogen atom.
Q 10. Write the main cause of attenuation of ground waves. On what factors, does its maximum range of coverage depend ?
Q 11. Obtain the expression for the electric field at a point on the equatorial line of an electric dipole.
OR
Obtain the expression for potential energy of an electric dipole placed with its axis at an angle (θ) to an external electric field. What is the minimum value of the potential energy ?
Q 12. A light bulb is in turn connected in a series (a) across an LR circuit,(b) across an RC circuit, with an ac source. Explain, giving necessary mathematical formula, the effect on the brightness of the bulb in case (a) and (b), when the frequency of the ac source is increased.
SECTION C (3 Marks Questions)
SECTION C (3 Marks Questions)
Q 13 a). Define the terms ‘drift velocity’ and ‘relaxation time’ giving their physical significance.
b) A conductor of length L is connected across a dc source of emf E. If the conductor is replaced by another of the same material and area of cross-section but of length 5L, by what factor will the drift velocity change ?
OR
Two cells of emf and internal resistance ε1, r1 and ε2, r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expressions for the emf and internal resistance of a cell which can replace this combination.
Q 14. a) You are required to select a carbon resistor of resistance of 56 kΩ土 10% from a shopkeeper. What would be the sequence of colour bands required to code the desired resistor ?
b) Write two characteristic properties of the material of a meter bridge wire.
c) What precautions do you take to minimize the error in finding the unknown resistance of the given wire ?
Q 15. a) Why do we use a shunt to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter ?
b) A galvanometer of resistance 15Ω shows a full scale deflection on the meter scale for a current of 6 mA. Calculate the value of the shunt resistance required to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of range 0 – 6 A.
Q 16.a) A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’, moving with velocity ‘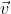 ’ is subjected to a uniform magnetic field
’ is subjected to a uniform magnetic field 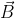 perpendicular to its velocity. Show that the particle describes a circular path. Obtain expression for the radius of the circular path of the particle.
perpendicular to its velocity. Show that the particle describes a circular path. Obtain expression for the radius of the circular path of the particle.
b) Explain, how its path will be affected if the velocity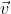 makes an angle θ (≠900 ) with the direction of the magnetic field.
makes an angle θ (≠900 ) with the direction of the magnetic field.
OR
Draw a schematic sketch of a cyclotron. State its working principle and write its two uses.
Q 17 .a) Explain the working of a compound microscope with the help of a labelled diagram.
Q 19 . a) Explain how a diffraction pattern is formed due to interference of secondary wavelets of light waves from a slit.
b) Sodium light consists of two wavelengths, 5900 Å and 5960 Å. If a slit of width 2 x 10-4 m is illuminated by sodium light, find the separation between the first secondary maxima of the diffraction pattern of the two wavelengths on a screen placed 1·5 m away.
Q 20 a) Draw a graph showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential for two different frequencies (v1 > v2) of the incident radiation.
b) Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain two features of photoelectric effect which cannot be explained by wave theory of light.
Q 21 Hydrogen atoms are excited with an electron beam of energy 12·5 eV. Find
a) The highest energy level up to which the hydrogen atoms will be excited.
b) The longest wavelengths in the (i) Lyman series, (ii) Balmer series of the spectrum of these hydrogen atoms.
Q 22 a) Write the principle of a semiconductor device which is used as a voltage regulator.
b) With the help of a circuit diagram explain its working.
c) Draw its I-V characteristics.
OR
a) Write the truth tables of (i) AND gate and (ii) NOT gate.
b) Show how an OR gate may be obtained with a combination of NAND gates.
Q 23 a) Draw the circuit diagram for studying the characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in common emitter configuration.
b)With the help of its input and output characteristics, how would you find the input resistance and the current gain from these characteristics ?
Q 24 a) Explain amplitude modulation of a sinusoidal carrier wave using a modulating signal, with the help of necessary diagrams.
b) For a given amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is 20 V and the minimum amplitude is 5 V. Calculate the modulation index.
SECTION D (5 Marks Questions)
Q 25 a) Obtain the expressions for the resultant capacitance when the three capacitors C1
b) In the circuit shown in the figure, the charge on the capacitor of 4 μF is 16 μC. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor of 12 μF capacitance.
b) Explain, how its path will be affected if the velocity
OR
Draw a schematic sketch of a cyclotron. State its working principle and write its two uses.
Q 17 .a) Explain the working of a compound microscope with the help of a labelled diagram.
b) Write the considerations that you keep in mind, while choosing lenses to be used as eyepiece and objective in a compound microscope.
Q 18 . Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image of an object by a convex lens. Using this diagram, obtain the expressions for the lens formula.
OR
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an erect image of an object kept in front of a concave mirror. Hence deduce the mirror formula.Q 19 . a) Explain how a diffraction pattern is formed due to interference of secondary wavelets of light waves from a slit.
b) Sodium light consists of two wavelengths, 5900 Å and 5960 Å. If a slit of width 2 x 10-4 m is illuminated by sodium light, find the separation between the first secondary maxima of the diffraction pattern of the two wavelengths on a screen placed 1·5 m away.
Q 20 a) Draw a graph showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential for two different frequencies (v1 > v2) of the incident radiation.
b) Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain two features of photoelectric effect which cannot be explained by wave theory of light.
Q 21 Hydrogen atoms are excited with an electron beam of energy 12·5 eV. Find
a) The highest energy level up to which the hydrogen atoms will be excited.
b) The longest wavelengths in the (i) Lyman series, (ii) Balmer series of the spectrum of these hydrogen atoms.
Q 22 a) Write the principle of a semiconductor device which is used as a voltage regulator.
b) With the help of a circuit diagram explain its working.
c) Draw its I-V characteristics.
OR
a) Write the truth tables of (i) AND gate and (ii) NOT gate.
b) Show how an OR gate may be obtained with a combination of NAND gates.
Q 23 a) Draw the circuit diagram for studying the characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in common emitter configuration.
b)With the help of its input and output characteristics, how would you find the input resistance and the current gain from these characteristics ?
Q 24 a) Explain amplitude modulation of a sinusoidal carrier wave using a modulating signal, with the help of necessary diagrams.
b) For a given amplitude modulated wave, the maximum amplitude is 20 V and the minimum amplitude is 5 V. Calculate the modulation index.
SECTION D (5 Marks Questions)
Q 25 a) Obtain the expressions for the resultant capacitance when the three capacitors C1
b) In the circuit shown in the figure, the charge on the capacitor of 4 μF is 16 μC. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor of 12 μF capacitance.
OR
a) Using Gauss’ law, obtain expressions for the electric field (i) inside, and (ii) outside a positively charged spherical shell.
b) Show graphically variation of the electric field as a function of the distance r from the centre of the sphere.
c) A square plane sheet of side 10 cm is inclined at an angle of 300 with the direction of a uniform electric field of 200 NC-1.Calculate the electric flux passing through the sheet.
Q 26 a) Obtain the expression for the average power dissipated in a series LCR circuit driven by an ac source of voltage V = Vm sin ωt supplying the current i = im sin (ωt + Φ).
b) Define the terms : (i) Wattless current, and (ii) Q-factor of LCR circuit.
OR
a) State Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
b) Derive an expression for the emf induced across the ends of a straight conductor of length l moving at right angles to a uniform magnetic field B with a uniform speed v.
c) Obtain the expression for the magnetic energy stored in a solenoid in terms of the magnetic field B, area A and length l of the solenoid through which a current i is passed.
Q 27a) Can two independent monochromatic light sources be used to obtain a steady interference pattern ? Justify your answer.
b) In a Young’s double-slit experiment, explain the formation of interference fringes and obtain an expression for the fringe width.
c) In an interference experiment using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensity of light of a point, where the path difference is λ, on the screen is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point when path difference is λ/4.
OR
a) Sketch the refracted wavefront for the incident plane wavefront of light from a distant object passing through a convex lens.
b) Using Huygens’ principle, verify the laws of refraction when light from a denser medium is incident on a rarer medium.
c) For yellow light of wavelength 590 nm incident on a glass slab, the refractive index of glass is 1·5. Estimate the speed and wavelength of yellow light inside the glass slab.




Comments
Post a Comment